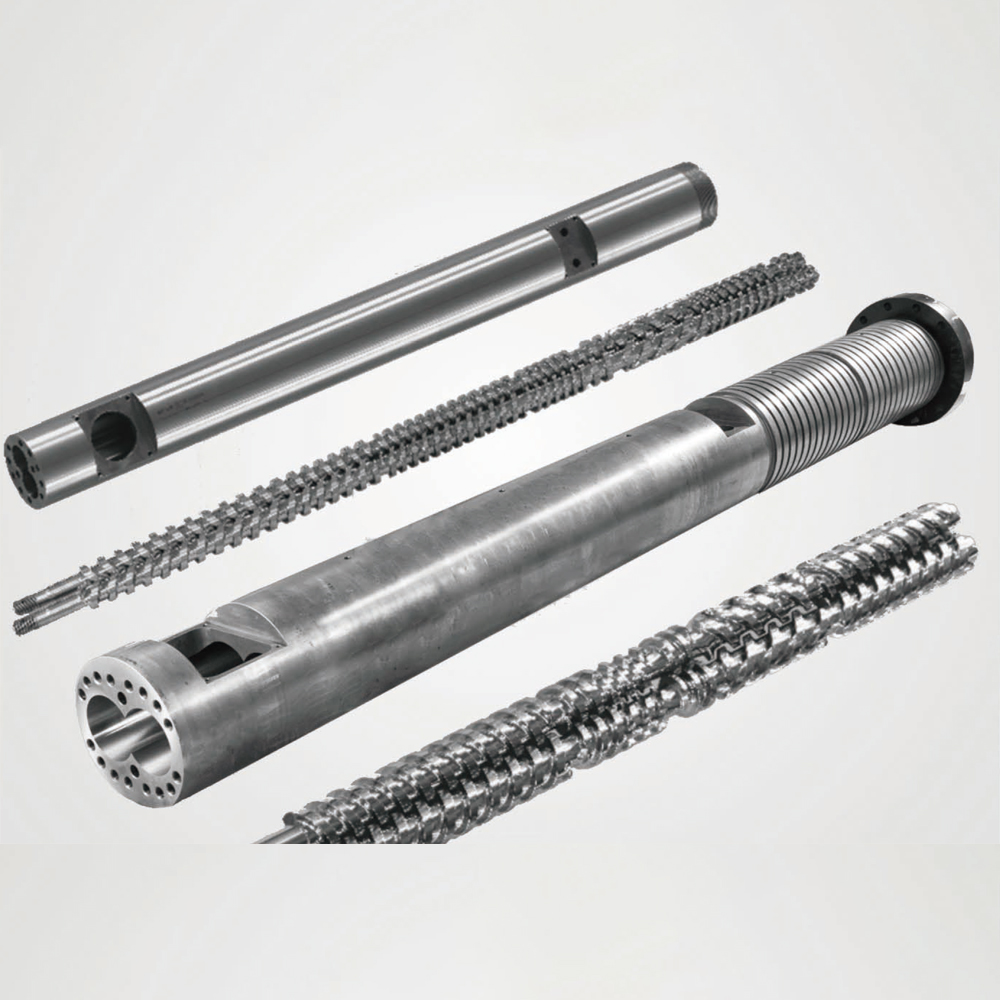
Parallel Twin Screw Barrel For Extruder

Construction: The parallel twin-screw barrel is typically made of high-grade alloy steel or other durable materials. It has a cylindrical shape and is precision-machined to ensure a close fit between the screws and the barrel. The interior surface of the barrel is often treated to resist wear and corrosion.
Screw Design: Each screw in the parallel twin-screw barrel consists of a central shaft and helical flights that wrap around it. The screws are modular, allowing for easy replacement or customization of individual screw elements. The flights of the screws are designed to intermesh with each other, creating multiple channels for material flow.
Material Mixing and Conveying: As the parallel screws rotate inside the barrel, they transport the plastic material from the feed section to the discharge section. The intermeshing action of the screws promotes efficient mixing, kneading, and dispersion of additives, fillers, and colorants within the plastic matrix. This results in uniform material properties and enhanced product quality.
Melting and Heat Transfer: The rotation of the parallel twin screws generates heat due to the friction between the plastic material and the barrel walls. This heat, combined with external heating elements embedded in the barrel, helps melt the plastic and maintain the desired processing temperature. The increased surface area of the intermeshing screws enhances heat transfer, enabling faster and more efficient melting.
Temperature Control: Parallel twin-screw barrels often incorporate a temperature control system to maintain precise temperature conditions during processing. This system typically includes heating and cooling elements, such as electric heaters and water jackets, embedded within the barrel. The temperature can be adjusted at different zones along the barrel to accommodate the specific requirements of the plastic material being processed.
Versatility: Parallel twin-screw barrels are highly versatile and can handle a wide range of plastic materials, including rigid and flexible plastics, as well as various additives and fillers. They are commonly used in applications such as compounding, extrusion, recycling, and pelletizing. Their design allows for high output rates and efficient processing.
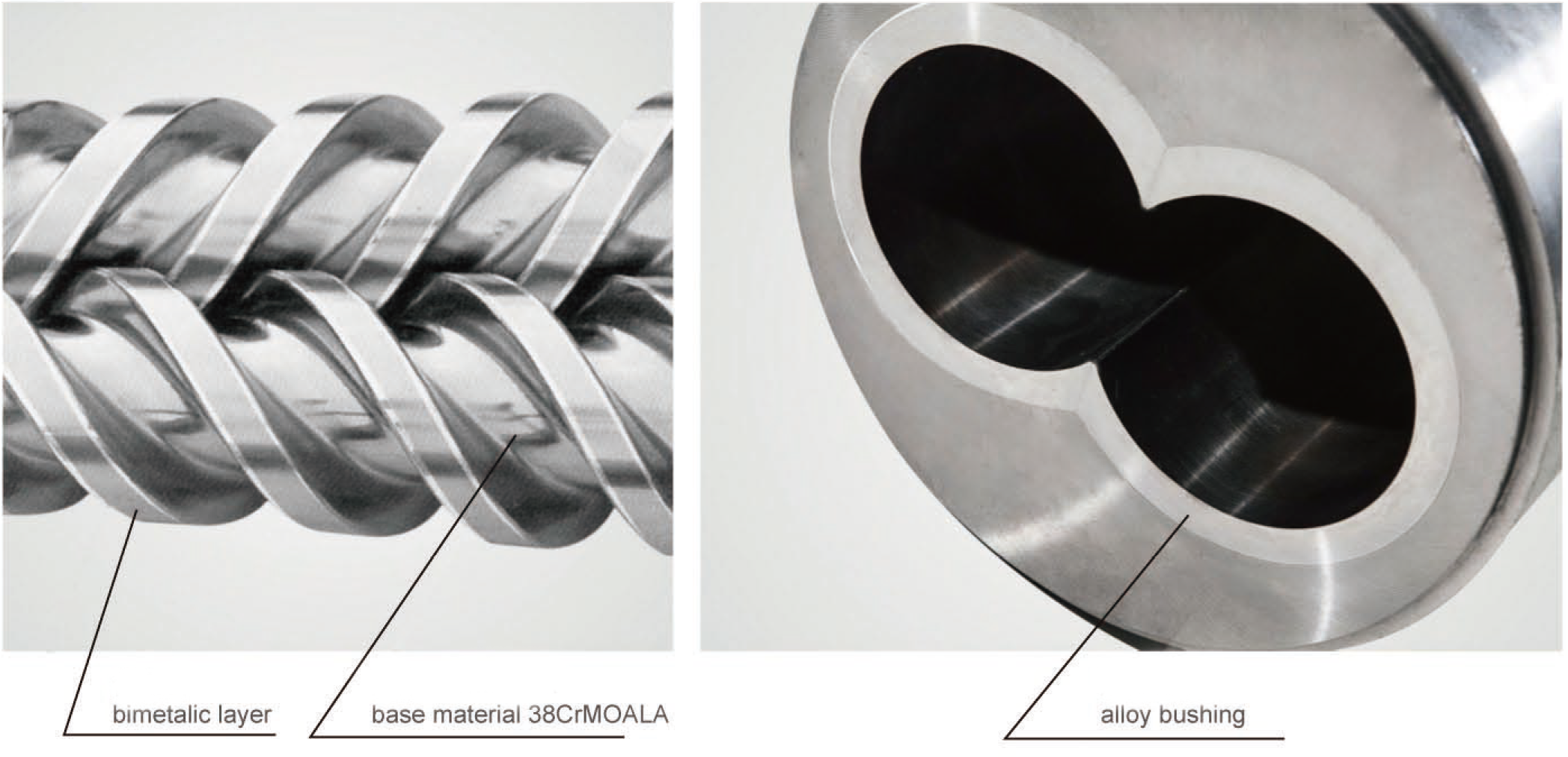
In summary, a parallel twin-screw barrel is an essential component in twin-screw extruders, providing efficient material mixing, melting, and conveying capabilities. Its design promotes uniformity, productivity, and versatility in plastic processing operations











